What is ear pinning Surgery?
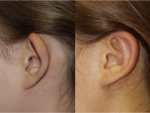
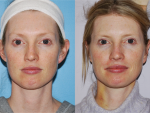
Ear pinning surgery, or Otoplasty, is a procedure to correct protruding ears. It involves reducing the size of the ear cartilage and securing it closer to the head. The surgery can be done on children or adults. Ear pinning surgery aims to create a more natural-looking ear and improve self-confidence. The results of the surgery are usually permanent.
Overly protruding ears or “lop ears” can be a source of teasing and self-confidence problems for children and adults. Through a simple operation, called otoplasty (or ear pinning), the shape and position of the ear can be modified to create a normal appearance. Although otoplasty is commonly performed on children in the pre-school or early school-age years, the procedure can provide significant benefit to adults with similar problems.
How much does Ear Pinning cost?
Otoplasty surgery costs can range from $3,000 to $6,000 depending on the surgeon’s fee, the anesthesia fee, and other related expenses.
How Dr. Sidle Performs Ear Pinning Surgery?
Dr. Sidle’s incision for the procedure is hidden behind the ear. The shape of the cartilage is changed through cartilage reshaping and the placement of sutures. After surgery, a small dressing is maintained for a few days. Swelling, bruising, and discomfort are typically mild and short-lived.
Why Prefer Dr. Sidle For Ear Pinning Surgery?
Experience Matters. As a board certified Facial Plastic Surgeon at Northwestern with expertise in the face and neck, Dr. Sidle can provide you with an individualized plan to achieve your goals of a more youthful face. Call our office for a one-on-one consultation.
Otoplasty (Ear Pinning Surgery) FAQs
Otoplasty surgery is usually performed by a qualified plastic surgeon. The surgeon makes a small incision behind the ear and removes some excess skin and cartilage. The surgeon then shapes the cartilage and closes the incision with stitches.
The surgeon makes a small incision in the back of the ear and then reshapes the cartilage to create a more aesthetically pleasing shape. Sutures hold the new shape in place, and the ears are typically bandaged following surgery. The procedure usually takes 1-2 hours to complete, depending on the extent of work that needs to be done.
Yes, Otoplasty is a safe and common surgery performed to correct protruding ears, usually in children, but it can also be done in adults. There are risks associated with any surgery, some of the potential risks in Otoplasty include bleeding, infection, and scarring. Most people experience excellent results from this procedure and are very happy with the outcome.
Full healing takes about six weeks, but you will likely feel better sooner than that. Most of the swelling and bruising should subside within the first week or two, but it may take a little longer for the incisions to fully heal. You must avoid strenuous activity for at least six weeks and avoid sun exposure until the scars have healed.
Most people report significant relief from the pain within 24 to 48 hours after surgery. However, some amount of soreness and discomfort is to be expected for several days following the procedure. Swelling may also persist for a week or two. It is important to follow your doctor’s post-care instructions carefully to ensure a speedy and safe recovery.
Insurance plans do not typically cover cosmetic procedures such as Otoplasty. However, some insurance companies may offer coverage for the procedure under certain circumstances (e.g., if the surgery is performed to correct a congenital disability or deformity).
If you are interested in undergoing Otoplasty, we recommend you speak with one of our financial coordinators to explore your payment options, or click here to see payment plan options.
It is typically recommended that a headband be worn for 4-6 weeks, especially at night following Otoplasty. This will help keep the ear in its new position and minimize the chances of returning to its original place. This will also help to ensure proper healing and reduce the risk of complications.
Most people feel better if they sleep with their heads elevated for the first few nights after surgery. This helps to reduce swelling and bruising. It is also a good idea to avoid sleeping on your side for the first two weeks, as this can put pressure on the ears. Be sure to use a cold compress on the ears for the first 48 hours following surgery. This will help to minimize swelling and discomfort.
No, Otoplasty is not a painful procedure. There may be some discomfort and soreness after the surgery, but this can be relieved with pain medication. Itching is another typical feeling after ear pinning surgery. Don’t rub or scratch your ears.
Yes, Otoplasty is a permanent procedure. Once the ears have healed, and the swelling has gone down, the results are generally outstanding and long-lasting. As a person ages, there may be minor changes over time, but overall, otoplasty results are permanent.
As with any surgery, there is always the potential for complications, including infection, bleeding, and scarring. It’s important to discuss your risk factors with your surgeon before surgery.
You can swim after 4-6 weeks. However, you should avoid swimming in chlorinated pools or oceans until the incisions have healed completely (which usually takes about 4-6 weeks). Swimming in a pool with chlorine can cause the incisions to heal prematurely and result in scarring. Oceans contain salt water, which can also harm healing incisions.
It depends on the individual, but typically ears are swollen for about two weeks after Otoplasty. During this time, it’s essential to avoid any strenuous activity or to bend over, as this can cause the ears to swell even more.
It’s also essential to keep the ears clean and dry. This can be done by using a gentle soap and water mixture to clean them and then dabbing them dry with a soft cloth. If the ears feel wet or sticky, you can use a small amount of baby powder to help absorb the moisture.
It is generally recommended that you sleep on your back for the first two weeks following Otoplasty. After that, you can sleep on your side but should avoid putting any pressure or weight on the ears. However, following your surgeon’s specific instructions about postoperative activity and sleeping position is important.
Yes, Otoplasty can be reversed. There are two ways to reverse Otoplasty: surgical and non-surgical. Surgical reversal involves returning the ears to their original position by performing another otoplasty surgery. Non-surgical reversal involves using tape or earrings to pull the ears back into place. Both methods have risks and benefits, so it is important to discuss the options with a healthcare professional before deciding.
You will need to avoid a few things after surgery. These include:
- No heavy lifting for six weeks
- Do not apply pressure to the ears (no headbands, hats, etc.) for four weeks
- Avoid blowing your nose for two weeks
- Avoid swimming and contact sports for at least four weeks
- Avoid sleeping on your side for the first two weeks after surgery.
The surgery is a short outpatient procedure and generally does not require any significant downtime. After your Otoplasty, you can return to work within 1-2 weeks, even though you may have to use a headband to hold your ears in place for a couple of weeks.
The results of Otoplasty will be natural because the surgery restores the ears to their natural position. In addition, otoplasty scars are typically well-hidden behind the ear. As a result, most people will not be able to tell that you have had surgery on your ears.
The ideal age to opt for Otoplasty is typically around 5 or 6. This is because the ears have reached their final size and are not still growing. Sometimes it is also recommended to wait until after puberty to perform Otoplasty, as the bones in the ear can continue to grow and change shape until around age 18.
Ultimately, it is important to consult with a qualified surgeon to discuss your specific needs for ear pinning surgery and find out what they believe would be the best age for your child to undergo Otoplasty.
It is preferred to use general anesthesia for Otoplasty because it provides the patient with a deeper level of sedation and results in less pain during and after surgery. However, regional anesthesia may be a better option for some patients, especially those who have anxiety about being put to sleep. Local anesthesia is generally only used for minor procedures.
Post-Operative Instructions
All post-operative instructions can be found on the Patient Resources page.
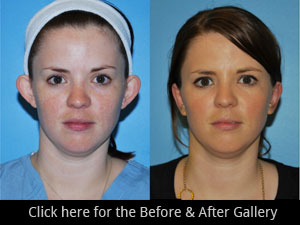
Our Results
Click Here to access our Before and After gallery for all procedures.